M0 on Solana: Technical Deep Dive
This document provides a detailed technical overview of the M0 Protocol's implementation on the Solana blockchain. It is
intended for developers who want to integrate with or build on top of $M and its extensions on Solana.
It assumes you are familiar with Solana's programming model (programs, accounts, CPIs) and have a conceptual understanding of M0's hub-and-spoke architecture.
Architecture & Core Components
M0's Solana deployment functions as a "spoke" in the cross-chain model, with Ethereum as the "hub". Communication and token transfers are managed by the M Portal, which is a customized implementation of Wormhole's Native Token Transfer (NTT) framework.
The system is composed of three core onchain programs and several offchain services that work in concert.
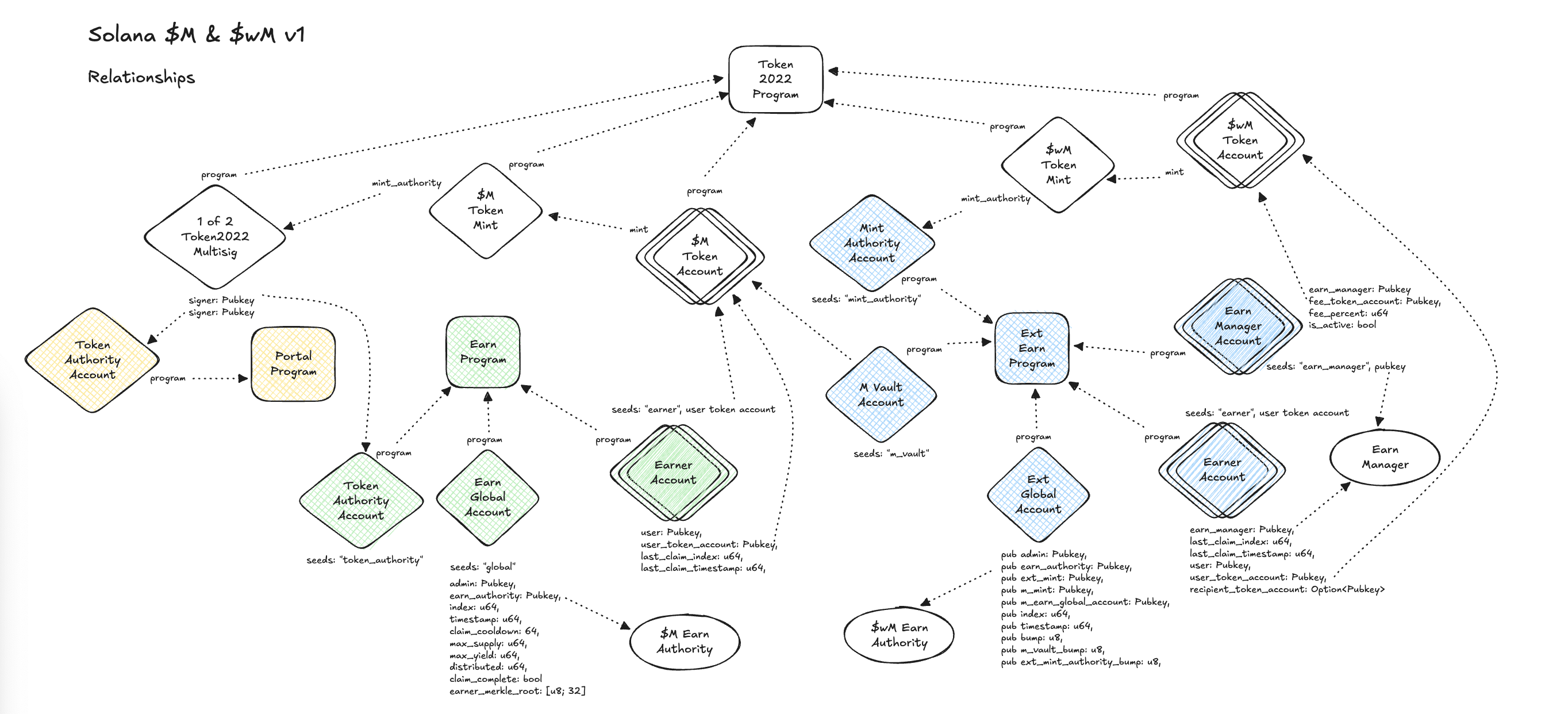
Onchain Programs
The onchain logic is modular, distributed across three main Solana programs written in Rust using the Anchor framework.
| Program | Mainnet Program ID | Devnet Program ID | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Portal | mzp1q2j5Hr1QuLC3KFBCAUz5aUckT6qyuZKZ3WJnMmY | mzp1q2j5Hr1QuLC3KFBCAUz5aUckT6qyuZKZ3WJnMmY | The gateway for bridging $M between EVM chains and Solana. A fork of Wormhole's NTT program with M0-specific payload support and executor integration. |
| Earn | MzeRokYa9o1ZikH6XHRiSS5nD8mNjZyHpLCBRTBSY4c | MzeRokYa9o1ZikH6XHRiSS5nD8mNjZyHpLCBRTBSY4c | Manages yield distribution and earner permissions for the base $M token with frozen-by-default security model. |
| M Extensions | 3C865D264L4NkAm78zfnDzQJJvXuU3fMjRUvRxyPi5da | 3C865D264L4NkAm78zfnDzQJJvXuU3fMjRUvRxyPi5da | Unified extension framework (m_ext) compiled with feature flags for NoYield, ScaledUi, and Crank models. |
| Swap Facility | MSwapi3WhNKMUGm9YrxGhypgUEt7wYQH3ZgG32XoWzH | MSwapi3WhNKMUGm9YrxGhypgUEt7wYQH3ZgG32XoWzH | Permissioned router for atomic swaps between whitelisted M0 extensions (ext_swap program). |
Key Onchain Assets
| Asset | Mainnet Mint Address | Devnet Mint Address | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| $M Token | mzerokyEX9TNDoK4o2YZQBDmMzjokAeN6M2g2S3pLJo | mzeroZRGCah3j5xEWp2Nih3GDejSBbH1rbHoxDg8By6 | The base yield-bearing stablecoin, implemented as a Token-2022 asset with frozen-by-default security. |
| $wM Token | mzeroXDoBpRVhnEXBra27qzAMdxgpWVY3DzQW7xMVJp | mzeroXDoBpRVhnEXBra27qzAMdxgpWVY3DzQW7xMVJp | The wrapped, 1:1 $M-backed extension using the Crank model, also a Token-2022 asset. |
V2 Upgrades: What Changed
The V2 upgrade introduced seven major enhancements to the Solana implementation:
1. Direct Bridging to Extensions
What Changed: The Portal now supports a destination_token field in the AdditionalPayload, allowing users to
bridge directly to extension tokens (like $wM) instead of only receiving base $M.
Why It Matters: Eliminates the need for a separate wrap transaction after bridging, improving UX and reducing costs.
Technical Implementation:pub struct AdditionalPayload {
pub index: u64,
pub destination_token: [u8; 32], // NEW: Target mint address (M or extension)
pub earner_root: Option<[u8; 32]>,
}2. Frozen-by-Default $M
What Changed: All new $M token accounts are initialized with AccountState::Frozen using Token-2022's
DefaultAccountState extension.
Why It Matters: Enhances security by preventing unauthorized accounts from holding $M. Only approved earners
(verified via Merkle proof) can have their accounts thawed.
// $M mint is created with DefaultAccountState::Frozen
let default_state = DefaultAccountState {
state: AccountState::Frozen,
};3. Onchain Yield Distribution
What Changed: Yield distribution is now fully onchain via the scaled-ui mechanism, replacing V1's centralized distribution.
Why It Matters: Increases transparency and decentralization. All yield calculations and distributions are verifiable onchain.
Technical Implementation:- Yield distributed via scaled-ui mechanism
- Index updates propagated onchain
- Extensions automatically sync on wrap/unwrap operations
4. Permissionless Index Updates
What Changed: The sync() instruction for extension index updates is now permissionless—anyone can call it.
Additionally, anyone can bridge an index update, and extensions automatically sync on wrap/unwrap operations.
Why It Matters: Enables keeper bots and users to ensure yield indices are always up-to-date without relying on centralized services.
Who Can Call: Anyone (no signer required for sync, though accounts must be valid). Index updates can also be bridged permissionlessly.
5. Executor Support for Generic Bridge Messages
What Changed: Integration with Wormhole's executor pattern (executor-account-resolver-svm) enables arbitrary
cross-chain instructions to be executed atomically with bridge transfers.
Why It Matters: Unlocks advanced cross-chain composability, such as "bridge and stake" or "bridge and swap" in a single transaction.
Technical Implementation:- Portal validates executor messages
- Executor Account Resolver resolves required accounts
- Arbitrary CPI instructions executed after mint
6. Unified Extension Framework
What Changed: All extensions (NoYield, ScaledUi, Crank) are now compiled from a single m_ext program using Rust
feature flags.
Why It Matters: Reduces code duplication, simplifies auditing, and ensures consistent behavior across all extension types.
Feature Flags:[features]
no-yield = []
scaled-ui = []
crank = []7. Multi-Network Support (Fogo Compatibility)
What Changed: V2 architecture is designed to support both Solana and Fogo (Wormhole's native rollup) with minimal changes.
Why It Matters: Future-proofs the protocol for multi-network deployment and leverages Wormhole's native cross-chain capabilities.
Implementation: Feature flags enable Fogo-specific configurations without forking the codebase.
Program Specifications
1. Portal Program (programs/portal)
The Portal is the entry and exit point for $M into the Solana ecosystem.
Core Logic & Custom Payload
-
Core Logic: Based on Wormhole NTT, it validates Wormhole Verifiable Action Approvals (VAAs) and processes inbound/outbound transfers. The key inbound instruction is
release_inbound_mint_multisig, which mints$Mtokens and makes a CPI to theEarnprogram'spropagate_indexfunction. -
Custom Payload (
payloads/token_transfer.rs): The standardNativeTokenTransferstruct is extended with anAdditionalPayload. This is the most critical customization, allowing M0-specific data to be securely transmitted with every bridge transfer.
// programs/portal/src/payloads/token_transfer.rs
pub struct AdditionalPayload {
pub index: u64, // Latest $M Earning Index from Ethereum
pub destination_token: [u8; 32], // Target token mint (M or extension)
pub earner_root: Option<[u8; 32]>, // Merkle root of approved earners
}index: The latest$MEarning Index from Ethereum.destination_token: The target token mint address on Solana (e.g.,$Mor$wM). NEW in V2.earner_root: An optional Merkle root of the official$Mearner list, as determined by M0 Governance on Ethereum.
Executor Integration
V2 Portal integrates with Wormhole's executor pattern to enable generic cross-chain instructions:
// Executor message structure
pub struct ExecutorMessage {
pub instruction_data: Vec<u8>,
pub program_id: Pubkey,
pub account_metas: Vec<AccountMeta>,
}The executor account resolver (executor-account-resolver-svm) resolves required accounts and executes instructions
atomically with bridge transfers.
2. Earn Program (programs/earn)
This program manages yield and permissions for the base $M token on Solana.
V2 Security Model: Frozen by Default
All $M token accounts are initialized with AccountState::Frozen. Accounts are only thawed after:
- User submits Merkle proof via
add_registrar_earner - Proof is verified against
earner_merkle_root - Account state is updated to
AccountState::Initialized
State (state/)
-
GlobalAccount (state/global.rs): A PDA seeded withb"global"that stores the program's configuration.admin: The administrative authority.earn_authority: A permissioned key that can callclaim_forinstructions.index: The most recently propagated$MEarning Index.claim_cooldown: The minimum time between yield claim cycles.max_yield&distributed: Used to track and cap the amount of yield distributed in a cycle.claim_complete: A flag indicating if the current claim cycle has finished.earner_merkle_root: The Merkle root of the governance-approved earner list.
-
EarnerAccount (state/earner.rs): A PDA seeded withb"earner"and the user's token account address. It tracks an individual's earning status.last_claim_index: The index at which the user last received yield.user: The wallet address of the earner.user_token_account: The specific token account that is earning yield.
Key Instructions (instructions/)
-
propagate_index: Called by the Portal via CPI. It updates theGlobalaccount'sindexandearner_merkle_root, and can initiate a new claim cycle if conditions are met (cooldown passed, new yield available). -
add_registrar_earner: A permissionless instruction allowing a user to prove their eligibility to earn yield. The user provides a Merkle proof that their address is included in theearner_merkle_root. On success, thaws the frozen token account. -
claim_for: A permissioned instruction called by theearn_authority. It calculates the yield owed to a specific earner since their last claim and mints new$Mtokens to their account. NEW in V2: fully onchain distribution. -
complete_claims: Called by theearn_authorityto mark the end of a yield distribution cycle. -
sync: NEW in V2. Permissionless instruction to update the earning index. Anyone can call this to keep indices current.
3. $M Extension Framework (programs/m_ext)
NEW in V2: Unified extension framework replacing separate programs for each model.
Architecture
All extension models are compiled from a single m_ext program using Rust feature flags:
// Cargo.toml
[features]
no-yield = []
scaled-ui = []
crank = []- NoYield Extensions: Compiled with
--features no-yield - ScaledUi Extensions: Compiled with
--features scaled-ui - Crank Extensions: Compiled with
--features crank(used by$wM)
State Structures
ExtGlobal Account (shared across all models):pub struct ExtGlobal {
pub admin: Pubkey,
pub earn_authority: Option<Pubkey>, // Only for Crank model
pub ext_mint: Pubkey,
pub m_mint: Pubkey,
pub m_earn_global_account: Pubkey,
pub bump: u8,
pub m_vault_bump: u8,
pub ext_mint_authority_bump: u8,
pub yield_config: YieldConfig,
pub wrap_authorities: Vec<Pubkey>,
}
pub struct YieldConfig {
pub variant: YieldVariant, // NoYield | ScaledUi | Crank
pub last_m_index: u64,
pub last_ext_index: u64,
}
pub enum YieldVariant {
NoYield,
ScaledUi,
Crank,
}// Only present when compiled with 'crank' feature
pub struct EarnManager {
pub manager: Pubkey,
pub fee_bps: u64,
pub fee_token_account: Pubkey,
pub bump: u8,
}
pub struct Earner {
pub user: Pubkey,
pub user_token_account: Pubkey,
pub recipient_token_account: Pubkey,
pub earn_manager: Pubkey,
pub last_balance: u64,
pub last_index: u64,
pub bump: u8,
}Core Instructions (Shared)
initialize: Sets up the extension's global statewrap(amount: u64): Wraps$Minto extension tokenunwrap(amount: u64): Unwraps extension token back to$Madd_wrap_authority/remove_wrap_authority: Manage wrap permissionstransfer_admin: Transfer admin control
Model-Specific Instructions
NoYield:claim_fees(): Admin claims all accrued yield
sync(): Permissionless index update (updates scaled-ui rate)set_fee(fee_bps: u64): Set optional fee (typically 0 for full pass-through)
add_earn_manager/remove_earn_manager: Admin manages earn managersadd_earner/remove_earner: Earn manager manages earnersclaim_for(user, snapshot_balance): Earn authority distributes yieldsync(): Update extension index from base $M programset_recipient: Earner sets custom yield recipient
4. Swap Facility (programs/ext_swap)
NEW in V2: Centralized router for atomic swaps between whitelisted extensions.
Global State
pub struct SwapGlobal {
pub bump: u8,
pub admin: Pubkey,
pub whitelisted_unwrappers: Vec<Pubkey>,
pub whitelisted_extensions: Vec<WhitelistedExtension>,
}
pub struct WhitelistedExtension {
pub program_id: Pubkey,
pub ext_global: Pubkey,
}Core Instructions
swap(amount, remaining_accounts_split_idx): Atomic cross-extension swapwrap(amount): Convert$Mto extensionunwrap(amount): Convert extension to$M(requireswhitelisted_unwrapper)whitelist_extension/remove_whitelisted_extension: Admin manages extensionswhitelist_unwrapper/remove_whitelisted_unwrapper: Admin manages unwrap permissions
- Only whitelisted extensions can participate in swaps
- Only whitelisted unwrappers can call
unwrapdirectly - All swaps maintain 1:1 peg
Developer Integration
Interacting via SDK
The recommended way to interact with the M0 Solana programs is through the official TypeScript SDK.
- Installation:
pnpm i @m0-foundation/solana-m-sdk - Core Classes: The SDK provides classes that abstract away the onchain complexity:
EarnAuthority: For admin-level actions like initiating claims and syncing indexes.EarnManager: For managing a set of earners within an extension (Crank model).Earner: For user-level actions and querying an individual's yield status.
import { EarnAuthority, Earner } from '@m0-foundation/solana-m-sdk';
import { Connection, PublicKey } from '@solana/web3.js';
import { createPublicClient, http } from 'viem';
// Setup clients
const connection = new Connection(RPC_URL);
const evmClient = createPublicClient({ transport: http(EVM_RPC_URL) });
// Load authority and earner
const auth = await EarnAuthority.load(connection, evmClient, M_EXT_PROGRAM_ID);
const earners = await auth.getAllEarners();
const earnerToClaim = earners[0];
// Build the claim instruction
const claimIx = await auth.buildClaimInstruction(earnerToClaim);
if (claimIx) {
// build, sign, and send transaction with the instruction...
}import { Program } from '@coral-xyz/anchor';
// Anyone can call sync to update yield indices
const tx = await program.methods
.sync()
.accounts({
extGlobal: extGlobalPDA,
extMint: extMintAddress,
mEarnGlobal: mEarnGlobalAddress,
mVault: mVaultPDA,
token2022Program: TOKEN_2022_PROGRAM_ID,
})
.rpc();
console.log('Synced yield:', tx);Offchain Data via API
For historical data, analytics, and building dashboards, use the M0 Solana API, which is powered by a Substreams indexer.
- Base URL (Mainnet):
https://api-production-0046.up.railway.app - SDK:
pnpm i @m0-foundation/solana-m-api-sdk -
Key Endpoints:
/events/bridges: Get latest bridge events./events/index-updates: Get historical$MIndex updates./token-account/{pubkey}/{mint}/claims: Get yield claim history for a specific token account.
Onchain Addresses
A full list of program IDs, mints, and other key accounts for both Mainnet and Devnet can be found in the Addresses resource page.
Fogo Network Support
NEW in V2: The architecture is designed to support Fogo, Wormhole's native rollup, alongside Solana.
What is Fogo?- Wormhole-native rollup optimized for cross-chain applications
- SVM-compatible (runs Solana programs with minimal changes)
- Optimized for low-latency cross-chain messaging
- Same program logic as Solana deployment
- Feature flags enable Fogo-specific optimizations
- Seamless interoperability with Solana via Wormhole NTT
Deployment Status: Fogo support is live. Check the Addresses page for Fogo-specific program IDs.
Source Code & Audits
- Portal & Earn Programs: m0-foundation/solana-m
- Extension Framework & Swap Facility: m0-foundation/solana-m-extensions
- Audits: Security audits for all programs can be found in the Audits resource page.
Next Steps
- Build with $M: Integrate the base
$Mtoken into your Solana dApp - Create an Extension: Deploy your own
$M-backed stablecoin using NoYield, ScaledUi, or Crank models

